With over 20 years in development and over $50 million invested in developing the methodology, KCS has produced significant benefits for support organizations around the world (dbkay.com)
What is Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS)?
Knowledge-centered service is a service delivery approach that emphasizes knowledge as a crucial resource for the organization.
It enhances the content of the knowledge based on demand and usage. In contrast, traditionally, we know that knowledge bases are created or purchased from someone else, and KCS states it is a waste of time and money. An organization can adopt other people’s knowledge that doesn’t apply to the customer base and how much knowledge will get leveraged or used to resolve the issue. Instead, ServiceNow KCS states that an organization should create that knowledge and improve it as it is demanded and based on the collective experience of the employees in the organization.
As in the service management industry, we have to leverage knowledge regularly, so this methodology focuses on creating, improving, and reusing that knowledge in a more structured and efficient manner.
KCS is also about collaboration and sharing as it is continuous improvement and finding efficient ways to solve customer's problems.
Unveiling the Power of Shared Knowledge: Empowering Organizations through Collaboration and Documentation
In most organizations, when a problem arises with the technical support group, they resolve it as they know how to resolve it. Still, nothing is documented, called “Tacid Knowledge,” which is not formalized or documented anywhere we haven’t written it down unless someone specifically asks about it.
Sharing this knowledge with others will not only improve but also build trust in the organization. People will now share their knowledge, making everyone smarter, more effective, and time-saving. Often, organizations will look at knowledge and consider it proprietary, as an expert can only create a knowledge article, but this is a fallacy. The people closest to work, the practitioners who resolve the issue daily and fulfill the customer’s request, have the most useful demand-driven knowledge. We need experts to fill in the gaps, but knowledge is most effective for those living it daily.
Organizations tend to make this mistake: before loading any system, they buy knowledge bases even without knowing whether that problem will arise in the future, and the knowledge bases are kept unused.
This problem of knowledge base was identified by the Consortium, which developed the KCS methodology.
There are four primary principles of KCS
- Abundance
- Create Value
- Demand Driven
- Trust
1. Abundance
More sharing leads to greater learning.
If a technical person well documents what he learned from his experience in solving a case or incident, it will be helpful to learn for more people across the organization.
2. Create Value
Holistic thinking and action.
We have to think holistically about what we are doing and how it contributes to the overall outcomes and the business objective we are trying to support. Having additional knowledge shared with other people will increase our value, overall outcomes, and objectives of our customers.
3. Demand Driven
Relevant knowledge should result from interaction.
Most of the knowledge bases are bought even before the system is introduced to the organization in the hope that all questions are answered in that knowledge base. However, in real time, the problems raised by consumers/customers may be different. So, in KCS, an article is written whenever there is a demand from the consumers. This is the opportunity to codify the tacit knowledge into the context that customer needs because they are to give us the language, they use to ask questions, and if we take that and put the knowledge into their context so that they can understand the answer. This can be very valuable to the next customer, who likely has a similar language or context to the first customer.
4. Trust
We can only create a successful practice via engagement, empowerment, and motivation.
Trust is the most important factor in KCS as we must trust our knowledge workers that knowledge will improve within the organization over time and will be valuable. We must trust the frontline workers who answer the calls resolving issues as day in day out processes. We have to trust that they know what they are doing and will create an efficient knowledge article from their experiences. The solution provided by them would address customers’ issues.
Core concepts of KCS
Transformation and continuous improvement
It involves the double loop process two types of the loop are the solve loop and the evolve loop.
Solve loop consists of Stages like Capture, Structure, Reuse, and Improve, which means that when knowledge is needed, it is captured and written in a structured format. Other consumers, customers, or agents reuse it.
Evolve loop consists of health content, Process Integration, Performance Assessment, Leadership, and Communication. In KCS, health content can be checked to determine whether the content is helpful to the organization using it. As part of Process Integration, if everyone is following the process within the organization to implement KCS. Performance Assessment whether the content is up to the mark, or we are adding unnecessary information in the KCS Article. All this is checked by the Leadership team within the organization. So, communication plays a significant role in both Double Loop Processes.
Buy-in at all Levels, Leadership, and Collective Ownership tell us that the whole organization is a part of the KCS Process. The frontlines of the organization are technical support and team managers. Everyone is involved in the KCS process.
KCS in ServiceNow
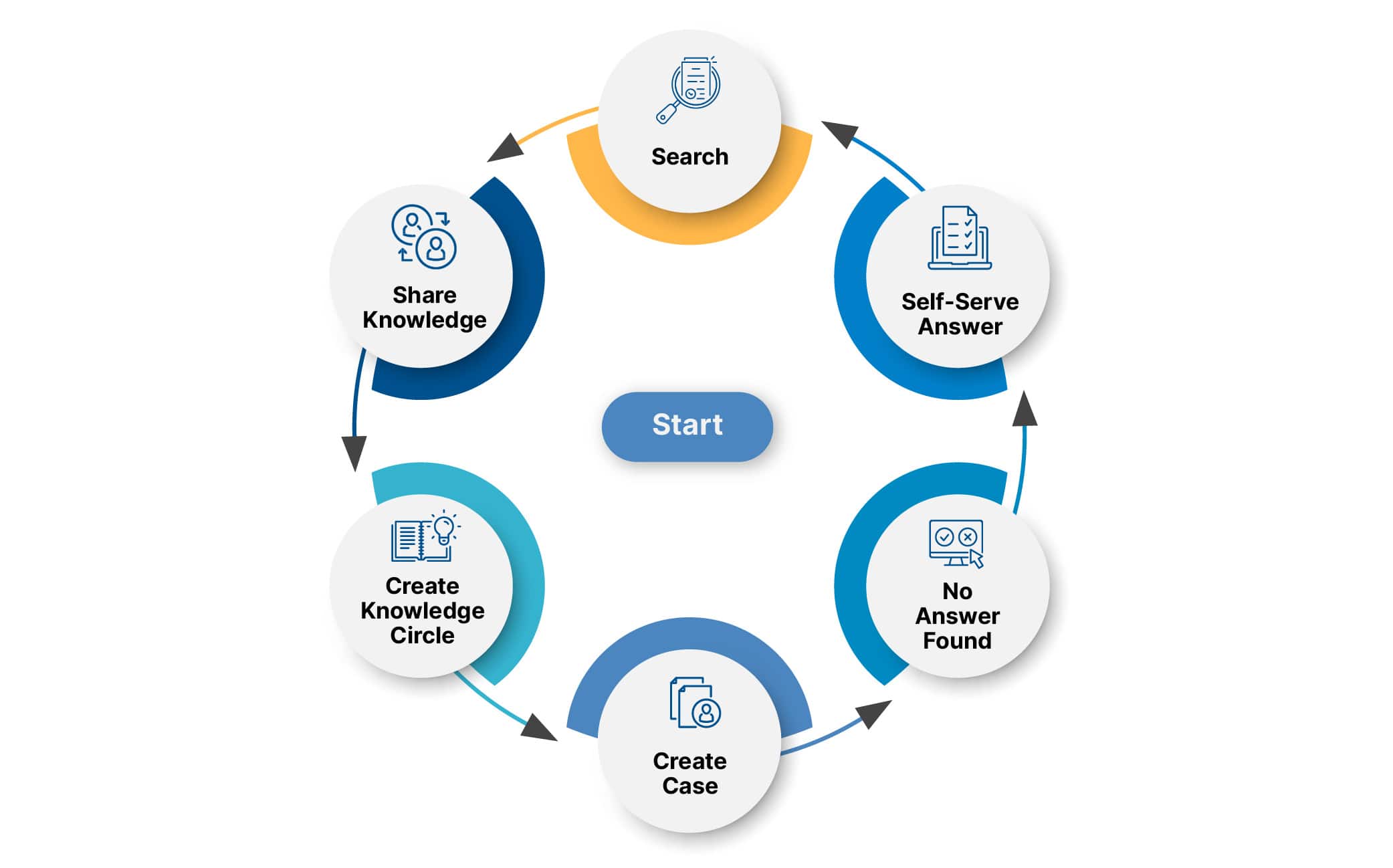
When a customer logs in to the portal and searches for their query in the Knowledge Base, they raise a case if the customer doesn’t find an answer. When the case is assigned to the agent and the agent resolves it, they will document it as an article shared again within the organization and categorized as internal or external. The internal article is used within the agents, and the External article is customer-facing, uploaded on the portal so everyone can access it.
KCS fields contain Issue, Environment, Cause, and Resolution.
Issue: Here, the issue is defined by the actual problem the consumer/customer faces.
Environment: What is the environment of the problem?
Cause: Cause is the actual cause of the issue.
Resolution: The resolution section provides the resolution steps to resolve the issue.
KCS States
KCS states involve Draft, Review or Scheduled for publish, Publish, Publish Retirement or Outdated, Retired states. KCS Knowledge manager, Knowledge contributor, Knowledge user, and Knowledge coach have various roles and responsibilities. The knowledge Manager manages the Knowledge Management system as a whole within the organization. Knowledge Contributor includes Technical Agent, Support Group which contributes to making KCS Article. Knowledge User includes who uses the knowledge Article.
Knowledge Coach takes up training on how to write an efficient article and trains the people within the organization, checks on the article, and gives a rating to the Articles through AQI.
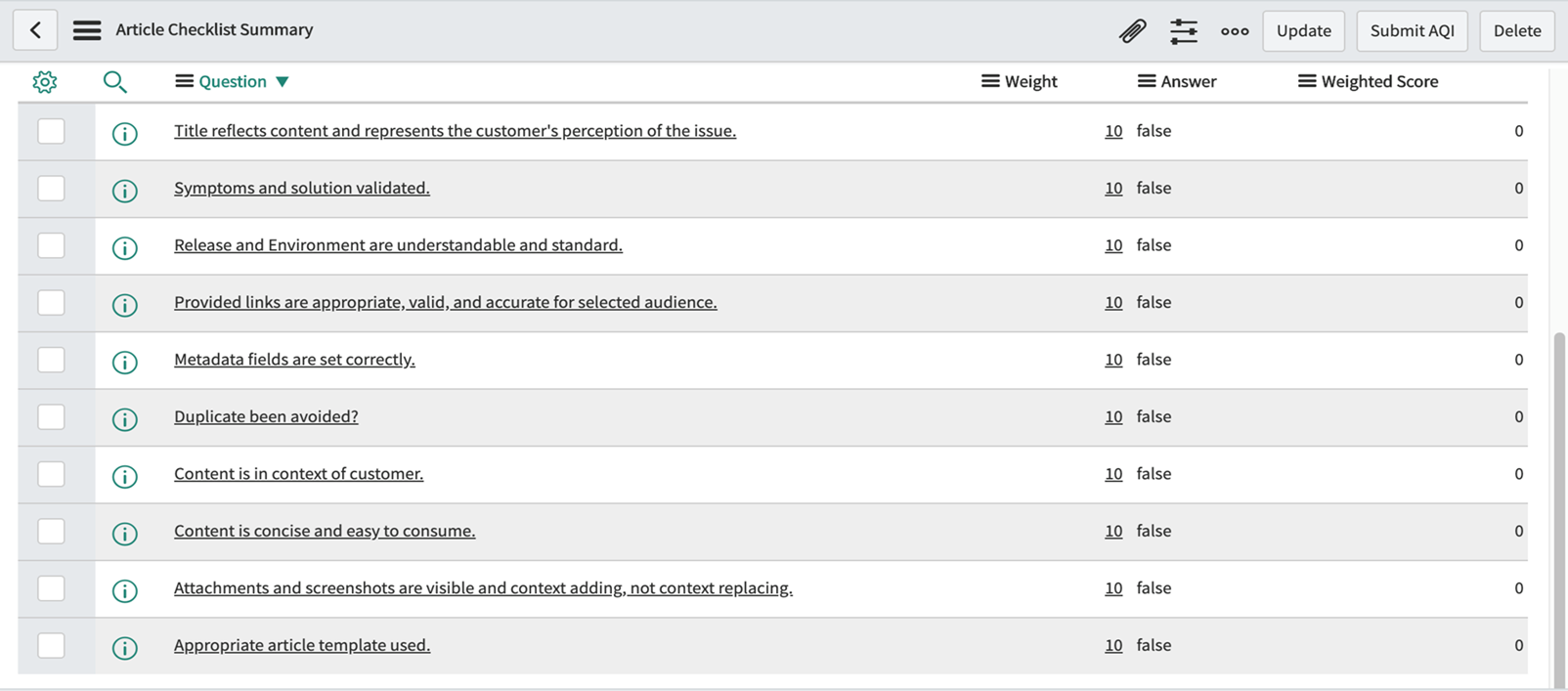
Article Quality Index (AQI)
This is the rating of the article given by higher authorities, which includes the manager and knowledge coach, who will assign a score out of 10 based on various parameters. Through this, the author will learn about the article’s quality, enhancing the Quality of Knowledge.
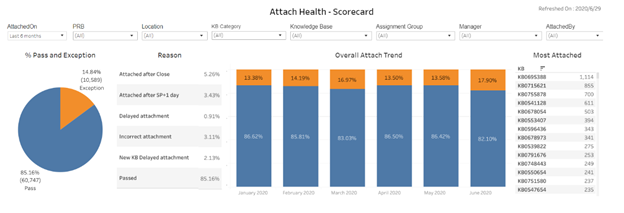
There are various reports and dashboards in ServiceNow that can be used to monitor the KCS system in the organization.
Advantages of KCS
Short-term advantages of KCS
- Faster resolution time, i.e., improved ability to process requests by customers
- Improvement in first-call resolution and reduced escalations
- Improvement in knowledge workers’ skills, job satisfaction , and confidence
Medium-term advantages of KCS
- Improvement in user success with self-service
- Training time is reduced for new employees joining the organization
Long-term advantages
- Overall Business improvement based on user experience patterns and Surveys Identify improvements in features, policies, and function
- Enable the usage of AI to improve user success in finding solutions
- Enable analytics that provide predictive and preventive capabilities (proactive customer engagement)
Conclusion
Knowledge-centered service (KCS) is a service delivery approach that places knowledge at the core of organizational operations. Developed over two decades with significant investment, KCS has proven beneficial for support organizations worldwide. This methodology emphasizes the creation, improvement, and reuse of knowledge in a structured and efficient manner. By shifting the focus from purchasing external knowledge bases to creating and evolving internal knowledge based on demand and usage, organizations can leverage the collective experience of their employees.
Click to learn more about Jade Global’s ServiceNow Professional Services













