In the fast-paced world of technology, the introduction of new services often brings with it significant Cloud infrastructure security concerns. Key issues include the potential for data loss and leakage, the misuse of credentials leading to unauthorized access, inadequate access controls, account hijacking, and the ever-present threat of malicious insiders.
Cloud service providers, including Oracle, leverage advanced, industry-leading security measures and operational protocols to safeguard their cloud offerings. To ensure the secure deployment and management of your workloads on Oracle Cloud, it is crucial to understand your security and compliance responsibilities.
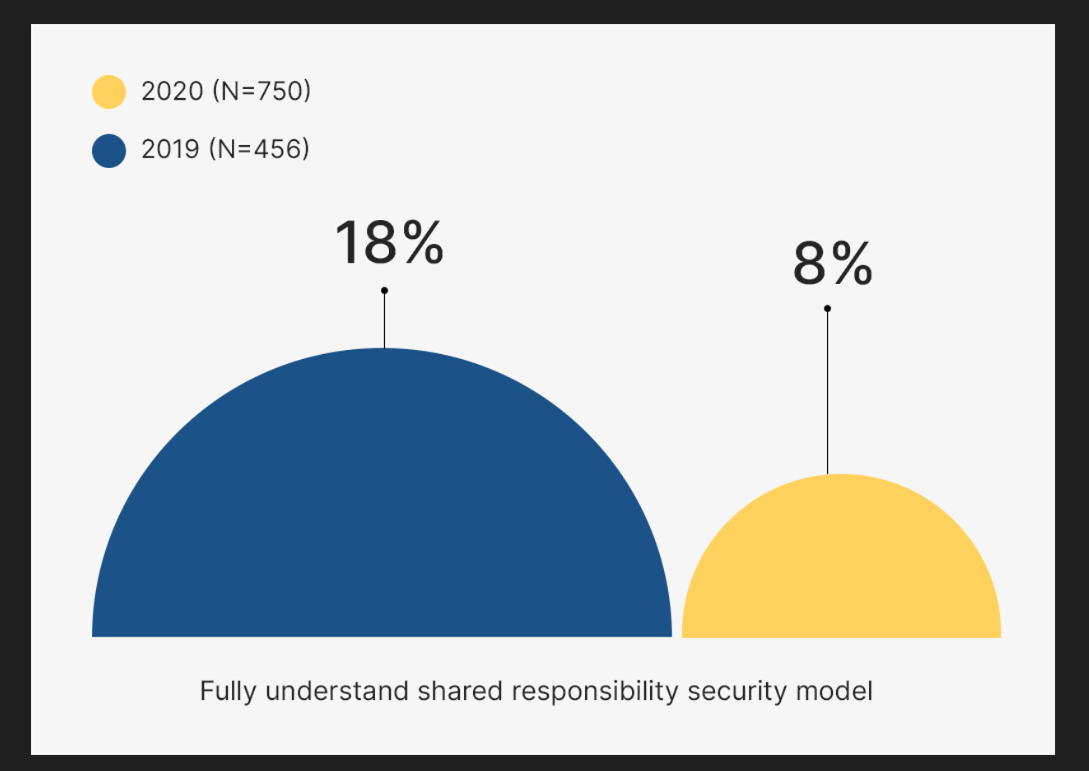
The Oracle and KPMG Cloud Threat Report 2020 highlights a concerning trend: the proportion of individuals confident in their understanding of the shared responsibility model for cloud infrastructure security has fallen from 18% in 2019 to merely 8% recently. This lack of clarity has inadvertently opened doors for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities in security measures designed to safeguard cloud data.
This blog aims to fortify cloud safety by shedding light on the collaborative security responsibilities between Oracle, your cloud provider, and you, the customer.
What is the Shared Responsibility Model?
The shared responsibility model is a framework used by Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) that outlines who is responsible for what in the cloud environment. This includes everything from the infrastructure and hardware to data, identities, workloads, networks, and settings. The model splits responsibilities between the CSP and its customers, with each provider having their own version of the model. Before we dive into the specifics of how two leading cloud providers approach this model, let's first explore why the shared responsibility model was created.
The Critical Role of the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Infrastructure Security
The shared responsibility model emerged as a crucial concept with the shift of organizations to cloud computing, where the need for secure environments became paramount. In the past, organizations managed their own data centers and were solely responsible for securing their infrastructure. However, as the reliance on cloud providers for hardware management increased, so did their role in ensuring platform security. This shift became especially significant after major security incidents, such as the vulnerability discovered in Azure's CosmosDB.
Cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) have since emphasized their commitment to maintaining secure environments. Despite these efforts, the limitations of their responsibility needed clarification, leading to the development of the shared responsibility model. This model delineates the boundaries of accountability, stating that providers are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, while customers must secure their data and applications within the cloud.
Benefits of the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Infrastructure Security
The shared responsibility model, despite its complexity, offers key advantages to both cloud service providers (CSPs) and customers:
Efficiency Gains: Under this model, CSPs typically manage the security of the hardware, infrastructure, and virtualization layers. This arrangement allows organizations to reallocate IT resources to other priorities, moving away from the extensive responsibilities of an on-premises setup.
Improved Security: Cloud providers prioritize the security of their platforms, investing heavily in monitoring, testing, and maintaining up-to-date systems. This commitment ensures enhanced protection for customer data and applications.
Access to Expertise: Partnering with CSPs gives customers access to advanced knowledge and skills in cloud security. This expertise helps in navigating the complexities of cloud security more effectively.
Key Strategies for Implementing the Shared Responsibility Model
Understand Your SLA: Each cloud provider's responsibilities vary, so thoroughly review your Service Level Agreement (SLA) to grasp your commitments. This is crucial for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring alignment, especially if you're utilizing multiple cloud services.
Integrate DevSecOps: Adopt DevSecOps to embed security throughout the software development lifecycle. This approach helps identify vulnerabilities early, streamlining the development process and reinforcing security.
Prioritize Data Protection: Data is invariably your most valuable asset. Regardless of the cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, etc.), safeguarding your data is always your duty. Start by securing your core data, classifying it, applying appropriate policies, and adjusting your security measures based on data sensitivity.
Maintain Open Communication: Stay alert to updates and communications from your cloud provider, as these can impact your security responsibilities. Don't hesitate to seek clarification or assistance when needed.
Leverage Expertise: Consider partnering with specialized security services. Tools and solutions such as Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM), Data Security Posture Management (DSPM), Cloud Workload Protection, and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) can significantly bolster your security posture within the shared responsibility framework.
Why Choose Jade Global for Oracle Cloud Services
With 20 years, Jade Global, an Oracle service partner, have honed skills to know what you need and what it takes to get there. With over 400 trained and certified Oracle Cloud Consultants, Jade has the expertise in Oracle Implementation Services to cater to your unique business requirements. We have the expertise to help you realize the benefits of Cloud with Oracle Implementation.
We have demonstrated key skills for successful Cloud implementations, and our offerings cover a wide range of ERP Cloud services. We can assist you in the beginning stages of defining a Cloud ERP strategy and help you optimize and extend your Oracle Cloud solution with Oracle PaaS. Know more.
Case Study: How Jade Global Enhanced Cloud Security for One of Its Clients
Recently, we had the opportunity to offer security assistance to one of our clients. Our comprehensive review unearthed several security vulnerabilities across different aspects of their cloud infrastructure security. Here's how we addressed these challenges:
1. Enhancing Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS)
IDCS is Oracle's Identity-as-a-Service solution, offering identity management, single-sign-on (SSO), and identity governance. Recognizing its crucial need for cloud security improvement, we implemented the following steps:
-
Elimination of Unnecessary Accounts and Groups: To reduce potential security risks, we deleted unwanted accounts and groups.
-
Creation of Role-Based Groups: We established groups based on roles, which streamlined the process of access management.
-
Activation of Multi-Factor Authentication: We enabled multi-factor authentication to introduce an extra layer of security.
-
Development of Custom Sign-In Policies: We created sign-in policies specifically tailored to our client's security needs.
-
Establishment of Network Perimeter Security: We set up a network perimeter to protect against external threats.
2. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Security Compute Instances
Our analysis highlighted that several VM servers were publicly exposed to inadequate network security groups, presenting considerable risks. To address these vulnerabilities, we:
-
Implementation of Individual Private Keys: We assigned individual private keys to each resource, avoiding the use of common keys.
-
Restriction of VM Server Access: We restricted access to VM servers by allowing only certain IP addresses.
-
Scheduling of OS Updates: We utilized the OCI OS Management service to regularly update all security patches.
-
Use of OCI Load Balancer: We employed the OCI Load Balancer to conceal actual server details from external parties.
3. Securing Publicly Exposed Web Applications
Several web applications running on OCI VM were discovered to be publicly accessible. To secure these critical business applications, we took the following actions:
-
Migration to Private Subnets: We migrated all applications from public to private subnets, using OCI load balancers for internet exposure.
-
Implementation of a Web Application Firewall (WAF): We implemented WAF to shield applications from harmful and unwanted internet traffic, ensuring uniform rule enforcement across a customer’s applications.
-
Conducting Vulnerability Scanning: We performed comprehensive scans to identify and fix security vulnerabilities, strengthening the applications against potential threats.
End Note:
Securing a cloud environment under Oracle's Shared Responsibility Model necessitates a collaborative effort. With Oracle providing a robust infrastructure foundation, customers must engage in strategic planning, diligent implementation, and continuous monitoring. This partnership is essential for creating a secure cloud ecosystem, enabling organizations to confidently adapt to cloud infrastructure security solutions and ensure a resilient operational framework.
Discover how we can elevate your cloud infrastructure security and revolutionize your business productivity. Click here to learn more!













